Our Research Group at AI@DEI 2025 – From Research to Industry
Last week our research group took part in AI@DEI 2025 – From Research to Industry, the annual event organised by the Department of Information Engineering (DEI) of the University of Padova and the Regional Innovation Network IMPROVENET, with the support of UniSMART.
The initiative aims to strengthen the dialogue between academia and industry, showcasing concrete applications of Artificial Intelligence across a wide range of sectors, from computer vision to predictive maintenance, industrial decision-making, robotics, automation, and conversational technologies.
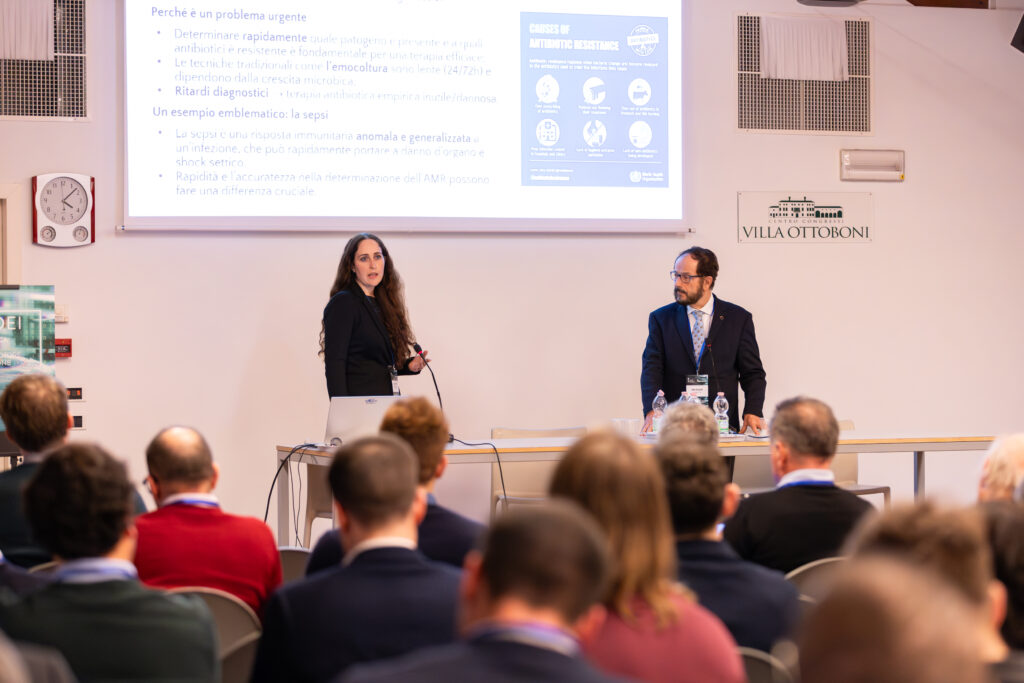
As part of the programme, our researcher Erica Tavazzi delivered the presentation: “Fondo Italiano per le Scienze Applicate: AI e diagnostica avanzata nella partnership DEI–AB Analitica contro l’antibiotico resistenza”.
The talk, prepared together with Dino Paladin (AB Analitica), introduced READY – Responsive Early Antibiotic resistance Detection and therapY, the project funded by the Italian Applied Sciences Fund (FISA) and launched this year. READY focuses on integrating AI, automation, and advanced diagnostics to support the early detection of antimicrobial resistance.
We warmly thank DEI, IMPROVENET, and UniSMART for organising the event, as well as all participating companies and colleagues for the productive exchange of perspectives.
A special acknowledgement goes to Sara Brugnerotto, whose photos beautifully captured the atmosphere of the day.

2nd progress meeting of the REDDIE project @UNIPD
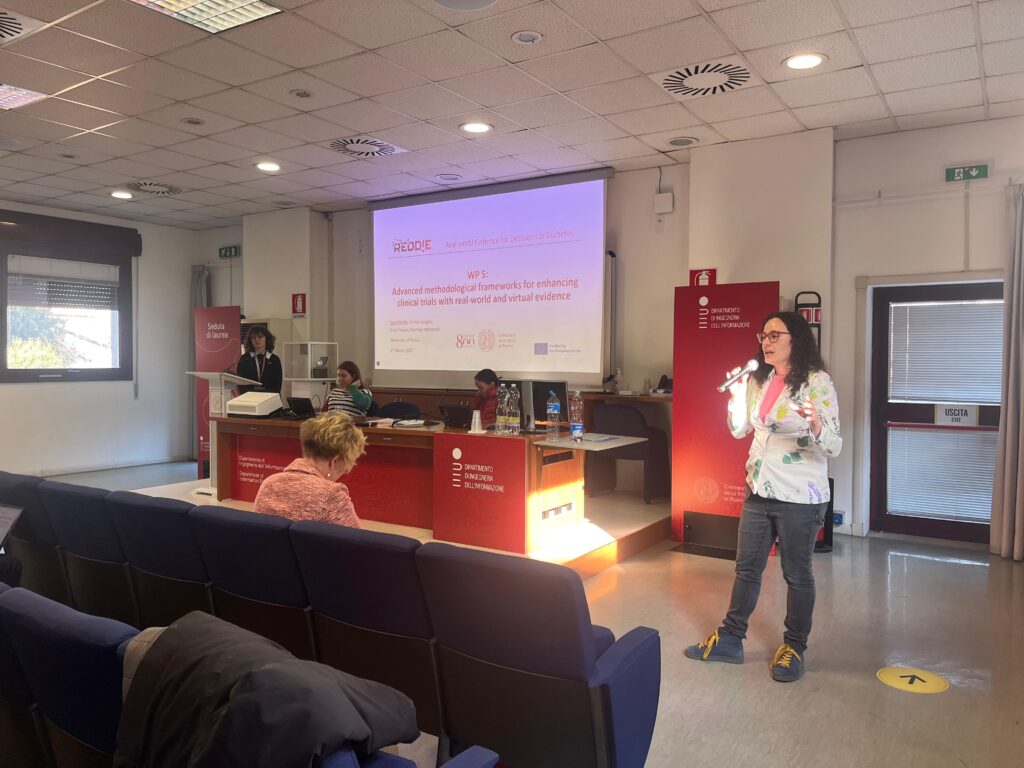
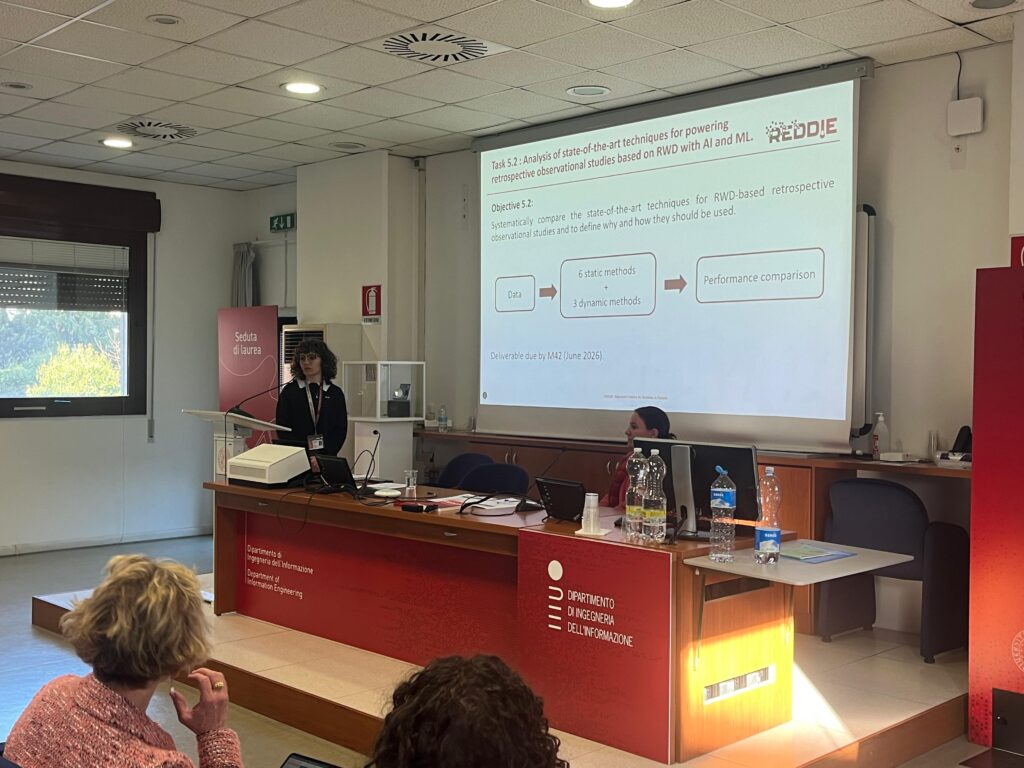
In the past few days, we had the pleasure of hosting the second progress meeting of the Horizon Europe REDDIE project at our Department of Information Engineering. Over two days of discussions, we reviewed progress across work packages, shared insights on emerging results, and conducted workshops on key challenges within each WP.
It was a fantastic opportunity to welcome our international partners, exchange ideas in person, and strengthen collaborations—while also enjoying good food and the first signs of spring in Padua! 😊





Guazzo A, Longato E, Trescato I, Tavazzi Er, Chiò A, Manera U, Zocco G, Cavalla P, Vercellino M,Ahmad L, Tavazzi El, Bergamaschi R, Padman R, Di Camillo B. Predicting Multiple Sclerosis Worsening Using Stratification-Based and Time-Dependent Variables Extracted from Routine Visits Data. In: Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science: 10th International Conference, LOD 2024, Castiglione della Pescaia, Italy, September22–25, 2024, Revised Selected Papers, Part II, Lecture Notes in Computer Science (LNCS) 2025.
2nd Annual Meeting of the DARE Initiative
On 20-21 February 2025, the Istituto Ortopedico Rizzoli in Bologna hosted the 2nd Annual Meeting of the DARE – Digital lifelong prevention initiative – Spoke 3 on Digitally Enabled Secondary and Tertiary Prevention. The event gathered researchers, clinicians, and experts working on innovative digital health solutions to enhance disease prevention and early diagnosis.
Our researcher Enrico Longato presented our latest work within Work Package 3 (WP3), focusing on the development of AI-driven digital tools for kidney disease prediction in diabetes. These tools leverage data and computational models to support personalised and data-driven healthcare approaches, aligning with the broader goals of the DARE Initiative.
We are proud to contribute to this important initiative and to collaborate with a multidisciplinary network of researchers committed to advancing digital health. The meeting provided a valuable opportunity for discussions, knowledge exchange, and new perspectives on integrating AI into clinical workflows.
We look forward to further developments and continued collaboration within the DARE Initiative.

Building Bridges Between Engineering and Medicine Through AI
On Tuesday, 21 January 2025, the Aula Morgagni at the Policlinico Universitario of Padua hosted the event “Introduction to Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.” Organised by the Departments of Information Engineering (DEI) and Medicine (DIMED), the meeting brought together experts and researchers to discuss the transformative role of AI in healthcare.
The session was opened by Professors Gaudenzio Meneghesso, Director of the DEI, and Paolo Simioni, Director of the DIMED, who welcomed attendees and highlighted the interdisciplinary collaboration driving AI innovation.
The scientific programme included a series of engaging presentations:
- Introduction to Machine Learning by Prof. Barbara Di Camillo (DEI) provided a comprehensive overview of the fundamentals of machine learning and its applications in medical research.
- Applications to Clinical Records by Dr. Erica Tavazzi (DEI), a researcher from our group, explored AI-driven approaches to extracting insights from patient data.
- Applications to Imaging Data by Dr. Marco Castellaro (DEI) demonstrated how AI enhances diagnostic imaging techniques.
- Large Language Models and Generative AI and Chatbots were expertly discussed by Prof. Giorgio Satta (DEI), who highlighted their potential to revolutionise communication and support activities.
- Data Representation and Knowledge in Generative AI by Prof. Nicola Ferro (DEI) delved into the technical challenges and opportunities in knowledge-based systems.
The event concluded with a dynamic Q&A session, fostering lively discussions among attendees and speakers.

Showcasing Progress in Digital Health Research at the DARE Initiative Meeting
On 15 January 2025, the Aula Magna of the Department of Information Engineering hosted a meeting dedicated to the research efforts of UNIPD within Spokes 2 and 3 of the DARE (Digital Life-Long Prevention) initiative.
During the event, Professor Barbara Di Camillo presented the pilot project in which our research group is actively involved, titled “Digitally-Empowered Management of Type 2 Diabetes: From the Diagnosis to the Prediction of Complications.”
It was a privilege to contribute to this gathering, which highlighted the exceptional quality and scientific relevance of the ongoing projects within the DARE initiative. The exchange of ideas and insights reaffirmed the initiative’s potential to make significant strides in digital health research.

Season’s Greetings from the SysBioBiG Team!
The SysBioBig group wishes you a Merry Christmas and Happy Holidays!
Best of luck and success in the New Year! 🎄🎅🏻🎁✨

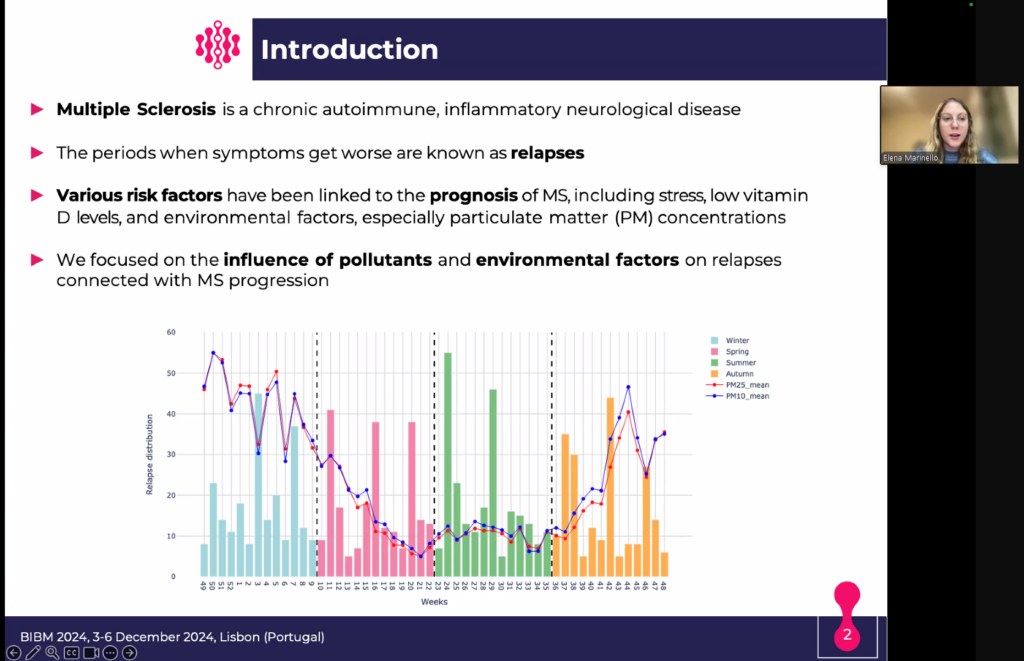
Unveiling the Impact of Pollutants and Weather Patterns on Relapses in Multiple Sclerosis: Insights from BRAINTEASER Presented at IEEE BIBM 2024
Last week, our PhD student Elena Marinello presented her research titled “Machine Learning Models Highlight the Impact of Pollution and Weather Patterns on Relapse Occurrence in Multiple Sclerosis Patients” at the Artificial Intelligence and Computational Methods for Public Health and the Environment workshop organised as part of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) 2024.
This study, conducted as part of the H2020 BRAINTEASER project, investigates how environmental factors, including pollution and weather patterns, contribute to predicting imminent relapses in multiple sclerosis. By leveraging clinical and environmental data from the week preceding potential relapse events, this research highlights the role of machine learning in advancing personalised medicine for MS patients.